How to scan new FC LUNS and SCSI disks in Redhat Linux without rebooting the server? Most of the Linux beginners have to wonder how to do this and this article will be for them. It may look very simple as we perform this in daily operation to scan LUNS but the system has much work to do in the background when you execute storage scanning commands. Redhat says this type of scan can be distributive since it can cause delays while I/O operation timeout and remove devices unexpectedly from OS.
Scanning FC-LUN’s in Redhat Linux
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (scsiid command) Subscriber exclusive content A Red Hat subscription provides unlimited access to our knowledgebase of over 48,000 articles and solutions.
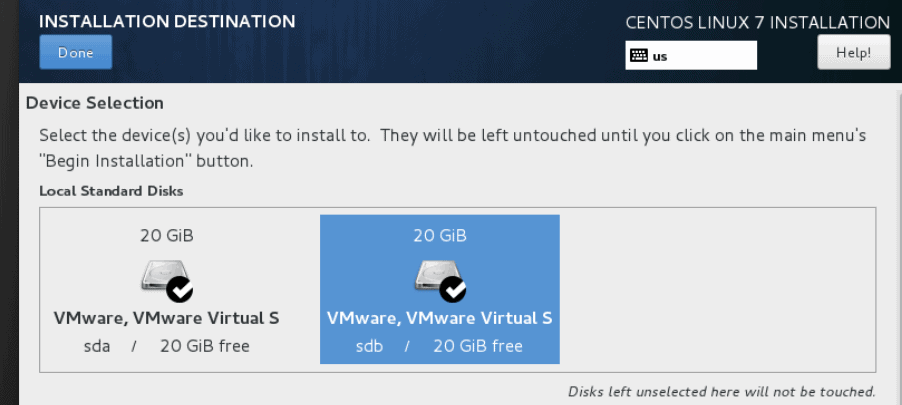
1.First, find out how many disks are visible in “fdisk -l” .
2.Find out how many host bus adapter configured in the Linux box.you can use “systool -fc_host -v” to verify available FC in the system.
- Oct 30, 2007 iscsi-initiator-utils RPM package – The iscsi package provides the server daemon for the iSCSI protocol, as well as the utility programs used to manage it. ISCSI is a protocol for distributed disk access using SCSI commands sent over Internet Protocol networks. This package is available under Redhat Enterprise Linux / CentOS / Fedora Linux and can be installed using yum command.
- In common with the SCSI protocol definitions Linux represents scsi addresses as a sequence of 4 ID numbers that uniquely identify the location of a SCSI device within the system. These are referred to as Host, Bus, Target, Lun (HBTL) or Host, Channel, Id, Lun (HCIL ) SCSI addresses.
In this case,you need to scan host0 & host1 HBA.
Download sindoh cameras. 3.If the system virtual memory is too low ,then do not proceed further.If you have enough free virtual memory,then you can proceed with below command to scan new LUNS.
Note:You need to monitor the “issue_lip” in /var/log/messages to determine when the scan will complete.This operation is an asynchronous operation.
You can also use rescan-scsi-bus.sh script to detect new LUNS.
Schlumbergersema driver.
4. Verify if the new LUN is visible or not by counting the available disks.
Redhat Scsi Scan
If any new LUNS added , then you can see more count is more then before scanning the LUNS.
Scanning SCSI DISKS in Redhat Linux

1. Finding the existing disk from fdisk.
2. Find out how many SCSI controller configured.
In this case, you need to scan host0,host1 & host2.
3. Scan the SCSI disks using below command.
4. Verify if the new disks are visible or not.
From Redhat Linux 5.4 onwards, Red hat introduced “/usr/bin/rescan-scsi-bus.sh” script to scan all the SCSI bus and update the SCSI layer to reflect new devices.
But most of the time, the script will not be able to scan new disks and you need to go with echo command.
Pro Tip: Load/access your all-time favorite Windows applications remotely from anywhere using your Linux system with virtual PCs by CloudDesktopOnline. For other more such innovative cloud products visit www.Apps4Rent.com.
Thank you for reading this article.
Redhat SCSI & RAID Devices Driver Download For Windows
Linux-IO (LIO) Target is an open-source implementation of the SCSI target thathas become the standard one included in the Linux kernel and the one present inRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7. The popular scsi-target-utils package is replacedby the newer targetcli which makes configuring a software iSCSI target quitedifferent.
In earlier versions one had to edit the /etc/tgtd/targets.conf file andservice tgtd restart. Here is an example configuration:
targetcli can be used either as an interactive shell or as stand alone commands.Here is an example shell session which creates a file-based disk image. Comments areprovided inline:
Hints:
- activating targetcli service at boot is mandatory, otherwise your configuration won’t be read after a reboot
- if you type
cdtargetcli will display an interactive node tree - after configuration is saved you don't need to restart anything
- the old scsi-target-utils doesn't support discovery authentication
- targetcli allows kernel memory to be shared as a block SCSI device via theramdisk backstore. It also supports 'nullio' mode, which discards all writes, and returns all-zeroes for reads.
- I'm having troubles configuring portals to listen both on any IPv4 addresses and any IPv6 addressesthe system has. I've still not figured that out entirely.
For more information please read Chapter 25 from Red Hat'sStorage Administration Guideor checkoutRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7 books on Amazon.
